Introduction to Automation in Manufacturing
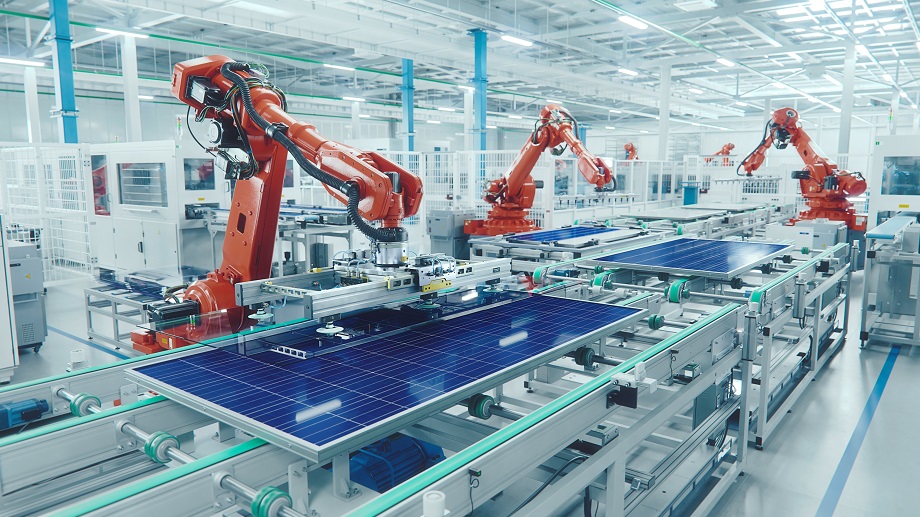
Automation has become an essential element of modern manufacturing, providing unparalleled efficiency and precision. Going back to the Industrial Revolution, the development of automation has been characterized by continual innovation and adjustment. Manufacturers have transitioned from simple mechanized processes to sophisticated systems that enhance every aspect of production. Today’s automation landscape is characterized by implementing advanced devices like the automatic tool changer, streamlining operations by minimizing downtime, and increasing precision. This technology allows for rapid tool switching, enabling machines to perform multiple tasks without human intervention, optimizing the production timeline, and addressing the ever-increasing demand for quicker, high-quality manufacturing outputs.
The Role of Advanced Tooling Solutions
Advanced tooling solutions are at the heart of the manufacturing revolution, offering unprecedented accuracy and speed across production lines. These solutions include state-of-the-art CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and robotic arms that ensure exactness in everything from automotive parts to microelectronics. Precision tooling is essential for maintaining high-quality standards in manufacturing and limiting defects and waste. By integrating new technologies like laser cutters and automated drillers, manufacturers can significantly enhance their capability to produce intricate and detailed components.
Benefits of Automation for Manufacturers
Adopting automation brings numerous benefits to the manufacturing industry, chief among them being increased productivity. Automated systems allow manufacturers to produce more units in less time while maintaining or improving quality, thus meeting consumer demands more efficiently. They also significantly reduce the potential for human error, leading to fewer defective products and less material waste. Moreover, automation can lower labor costs by reducing the need for a sizeable manual workforce. This, in turn, allows companies to invest more in skilled labor, focusing on roles that require critical thinking and technical expertise rather than repetitive tasks. The enhancement of workplace safety cannot be overstated either, as machines can take over dangerous tasks, protecting workers from hazardous environments.
Challenges in Implementing Advanced Tools
While the advantages of automated systems are clear, implementing these advanced tools presents several challenges. The high initial investment costs can be prohibitive, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises. This significant financial commitment often requires a detailed cost-benefit analysis to ensure a viable return on investment (ROI). Additionally, there is a need to retrain the existing workforce to operate and maintain these sophisticated machines proficiently, which can be time-consuming and expensive. Adapting to new technology also means overcoming resistance within the organization as employees adjust to changes in their roles. Furthermore, integrating new tools into existing production lines can be technically complex, requiring detailed planning and expertise to ensure seamless operations.
Emerging Trends in Manufacturing Automation
The manufacturing industry is at the cusp of a digital transformation, with emerging trends pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Incorporating the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) into manufacturing automation allows for the creation of ‘smart’ factories. These environments harness real-time data to optimize processes dynamically, reducing delays and improving decision-making. IoT devices enable machines and human overseers to interact with one another, promoting a dynamic and flexible environment. AI’s role in this context is swiftly analyzing vast amounts of data and predicting when machinery might require maintenance, thus minimizing unplanned downtime.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
In practice, the impact of automation across industries is profound and varied. In the automotive industry, robots perform precise welding tasks and assemble components with unmatched consistency, raising the bar for quality and efficiency. Automated systems conduct optical inspections in the electronics sector to ensure that each circuit board is impeccable. Beyond these sectors, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and textiles are also reaping automation benefits, showcasing its versatility and broad applicability. These real-world examples illustrate how automation reduces costs, minimizes errors, and delivers products quicker than ever, setting a new standard for excellence.
Expert Insights on Automation and Tooling
Experts in the manufacturing sector widely agree that the momentum toward automation and sophisticated tooling will keep climbing. As various industries increasingly acknowledge these technologies’ significant benefits, the manufacturing landscape is changing rapidly. Seasoned analysts envision a future where systems are designed around hybrid models—integrating humans’ intuitive capabilities with machines’ precise efficiencies. Rather than completely replacing human roles, this evolution emphasizes the importance of human oversight in automated processes.
This shift indicates a growing demand for jobs that require advanced technical skills, empowering the workforce to take on essential responsibilities in managing and refining these automated systems. Meanwhile, ongoing innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning are driving improvements in operational efficiency and accuracy, leading to unprecedented performance in manufacturing. The marriage of human intuition and machine precision promises to create a more prosperous, productive workplace environment where technology and human expertise work harmoniously.
Future Outlook: What’s Next for Manufacturing?
As manufacturers look to the future, the focus will likely intensify on developing more intelligent systems that can operate with complete autonomy while being user-friendly. Integrating advanced interfaces that facilitate seamless interaction between humans and machines is predicted to be at the forefront of these developments. Furthermore, the emphasis on sustainable practices is expected to grow, encouraging the development of machines and tooling systems that increase efficiency and reduce environmental impact. As these trends unfold, they promise to redefine global manufacturing, creating a landscape that is efficient, connected, and ever more innovative.
Stay updated with the latest tech news and trends at BuzzTelecast.